Imagine for a moment that your ability to remember tasks to be completed in the future could transform the way you work. Prospective memory then emerges as a key skill, impacting not only productivity but also the organization of a professional environment. In a context where increasing demands and workload weigh more heavily on employees, knowing how to anticipate upcoming actions becomes a valuable asset. By allowing one to remember tasks to be accomplished and deadlines to be met, this future-oriented memory plays an essential role in managing priorities and responsibilities. It revolves around two main mechanisms: event planning, when an event triggers an action, and time management, when the action is dictated by a specific moment. Numerous stages in projects, as well as the smooth progress of missions, therefore depend on our ability to use this memory effectively. Understanding its role and mechanisms thus provides invaluable insights for optimizing professional performance and adapting our approaches to contemporary challenges.

In the current professional context, where demands are constantly increasing and tight deadlines are the norm, anticipating future needs and managing tasks effectively becomes a primary challenge for companies. A study conducted by the 2023 Employee Health Barometer revealed that 62% of respondents associated their stress with intense workloads. Thus, the ability to absorb and apply the principles of prospective memory constitutes a major asset. But what does this imply concretely in the workplace?
Table des matières
ToggleProspective Memory: The Cornerstone of Task Management
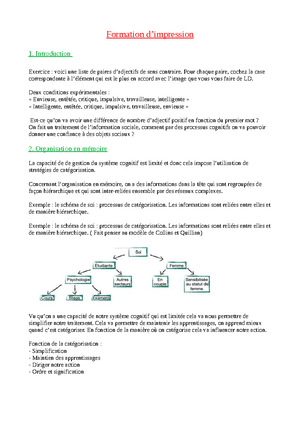
Prospective memory is defined as the cognitive process that allows an individual to remember to perform an action in the future, such as sending a report or calling a client. Unlike retrospective memory, which focuses on past events, prospective memory is oriented toward the future and plays an essential role in planning professional activities. Indeed, delving into the details of its functioning often refutes the idea that it is merely a simple recall ability. In reality, it relies on complex cognitive mechanisms, integrating both attention and intention management.
A study from the University of Melbourne in 2022 highlighted that professionals who use prospective memory techniques succeed in meeting 25% more deadlines than those who do not apply them. This underscores the significant impact of prospective memory on productivity. By incorporating this skill into the workplace, results can be particularly striking. For example, a project manager can anticipate when to check the progress of a team, without waiting for reminders. Similarly, a human resources manager may remember to send performance evaluations in order to meet deadlines set by management.
Concrete Practices to Improve Prospective Memory
To enhance this skill within teams, certain tools and methods prove particularly effective. First of all, it is crucial to integrate external aids into the professional routine. Using electronic reminders, task lists, or project management applications lightens the memory load while providing a clear structure of responsibilities. According to a study from MIT, teams that use collaborative tools see their efficiency increase by 30%, thanks to the clarity provided by these devices.
Next, structuring the workday by incorporating regular breaks is an excellent strategy. For instance, taking ten minutes every hour not only reduces cognitive fatigue but also recharges memory. A study from Stanford University showed that by integrating breaks into work, employees exhibit a 20% increase in their productivity. These moments of relaxation have a direct impact on the ability to remember future tasks.
Furthermore, limiting multitasking can also promote better prospective memory. The results of research from the University of California demonstrated that individuals who focus on a single task achieve better performance of at least 40% compared to multitasking work. In terms of planning, it is wise to schedule more complex tasks during times of low cognitive load. Additionally, regularly reviewing one’s priorities helps ensure that every event or task is connected to an intention, such as remembering to call a colleague once a task is well advanced.
In conclusion, the ability to anticipate and plan effectively in the professional environment largely relies on prospective memory. Integrating solid practices and utilizing appropriate tools allow for the optimization of this faculty. Ultimately, companies that can leverage this magical cognitive skill will be able to enhance their efficiency while alleviating the stress associated with task management. Promoting this capability engages in a dynamic and enriching process toward better performance within teams.

FAQ: Anticipating the Future with Prospective Memory
What is prospective memory? Prospective memory is the ability to remember to carry out a planned action in the future, such as calling a client or finalizing a report before a deadline.
Why is it important in the professional environment? It allows for meeting deadlines, tracking ongoing tasks, and maintaining project continuity, thus improving efficiency at work.
What are the types of prospective memory strategies? Strategies are divided into two categories: those based on events, which depend on a specific event, and those based on time, which concern a specific moment to perform an action.
What are the risks associated with prospective memory? It can be affected by distractions, stress, and fatigue, which diminishes our ability to remember future intentions.
How can one improve their prospective memory at work? It is advisable to use external aids, structure the day with breaks, limit multitasking, and regularly review priorities.
How can breaks help prospective memory? Regular breaks help reduce cognitive fatigue and enhance the ability to remember future tasks.
What is the importance of planning at work? Effective planning, taking into account prospective memory, facilitates collaboration and optimizes time management in a professional environment.