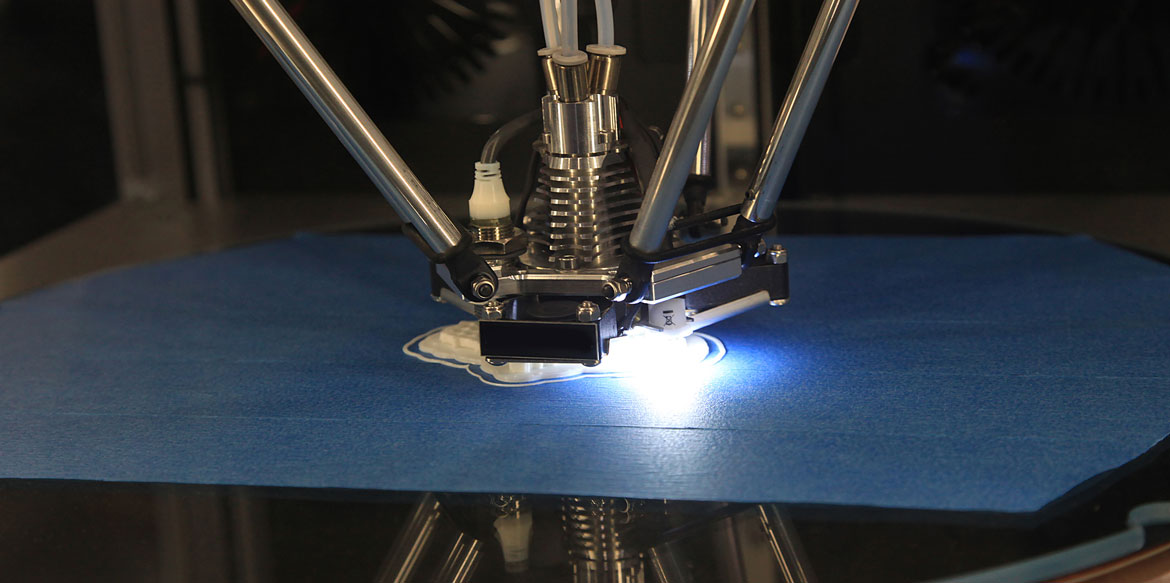
Additive manufacturing, often known as 3D printing, is revolutionizing the way objects are designed and produced. This innovative process relies on adding material layer by layer to create three-dimensional objects from a digital file. Increasingly used in industrial sectors, this technology plays a crucial role in optimizing manufacturing processes. It not only reduces costs and production time but also enhances product customization and complexity. Whether in aerospace, the automotive industry, or even medicine, the applications of additive manufacturing continue to expand, paving the way for a more agile and efficient era of production.
Additive manufacturing, more commonly known as 3D printing, is a cutting-edge technique that transforms how we design and produce objects. This process is based on the layering of successive materials to create three-dimensional objects from a digital file. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often involve removing material from a raw piece, additive manufacturing adds material. These materials can vary from plastic resin to metals and ceramics.
The objects created through additive manufacturing are modeled from digital data, often produced using computer-aided design (CAD) software. Once the model is complete, the 3D printing machine reads this digital data to guide the extrusion of material, layer by layer. This approach opens up immense possibilities in terms of customization and complexity of shapes, which were previously difficult to achieve with more traditional processes.
Additive manufacturing presents a multitude of advantages. Firstly, it helps reduce material waste, as only the necessary materials are used during the process. Additionally, it offers great flexibility in design and production, facilitating on-demand manufacturing and product customization. This is particularly advantageous in sectors where customer needs vary greatly, such as the automotive and aerospace industries.
The challenges of additive manufacturing go beyond technical solutions. Integrated within the framework of Industry 4.0, it is accompanied by the use of machine learning to optimize production processes and improve operational efficiency. To learn more about this synergy between 3D printing and machine learning, check out our dedicated resource.
However, challenges also exist. The durability of prints, manufacturing speed, and standardization of processes are major concerns. The industries involved are seeking to develop solutions to improve these aspects while ensuring that the final products are reliable and meet quality standards. Furthermore, integrating additive manufacturing and smart contracts into the supply chain can provide increased transparency and traceability of products, thereby minimizing human errors.
In summary, additive manufacturing embodies a true revolution in the way we envision the creation and distribution of products. It meets the demands of a world increasingly focused on customization and efficiency. For professionals seeking to understand the dynamics of design and manufacturing in modern industrial environments, the case study of Stéarinerie Dubois may offer relevant insights into the practical application of these rapidly changing technologies.

Table des matières
ToggleFAQ: Discover additive manufacturing: definition and challenges
Q: What is additive manufacturing?
A: Additive manufacturing is an innovative process that allows the creation of three-dimensional objects from a digital file. This process relies on the successive addition of layers of materials to shape the final object.
A: Additive manufacturing works by layering materials, often through extrusion, to produce a three-dimensional (3D) object. Each layer is traced and fused to fit the previous one, creating a solid and complete piece.
A: The materials used in additive manufacturing are varied, ranging from plastics and metals to ceramics and composites. These materials are chosen based on the final use of the object, offering great flexibility and diversity in production.
A: The advantages of additive manufacturing include the ability to produce complex shapes, reducing waste, on-demand customization, and improving energy efficiency compared to traditional methods.
A: The challenges of additive manufacturing include the need to improve production speed, material quality, associated costs, and the integration of these technologies into existing production chains.
A: Additive manufacturing is widely used in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, healthcare, and even general manufacturing for the production of prototypes, spare parts, and customized components.