In an ever-evolving industrial landscape, the smart factory emerges as the shining star of the Industry 4.0 era. At the crossroads of technology, automation, and artificial intelligence, it redefines the contours of modern production. One of the most striking examples of this revolution is Siemens, a key player that harnesses the power of data and digital innovations to shape the future of industry. Through its advanced solutions, Siemens transforms its manufacturing processes into intelligent systems, thereby optimizing the efficiency, flexibility, and reliability of its operations.
This case study highlights the strategies and technologies implemented by Siemens to drive its digital transformation. By integrating data management tools and collaborative platforms, the company not only keeps pace with trends but also becomes a model to follow in the field. By examining Siemens’ innovative practices, we will delve deeper into the fascinating world of the smart factory and discover how the integration of Industry 4.0 changes the game for the industrial sector.

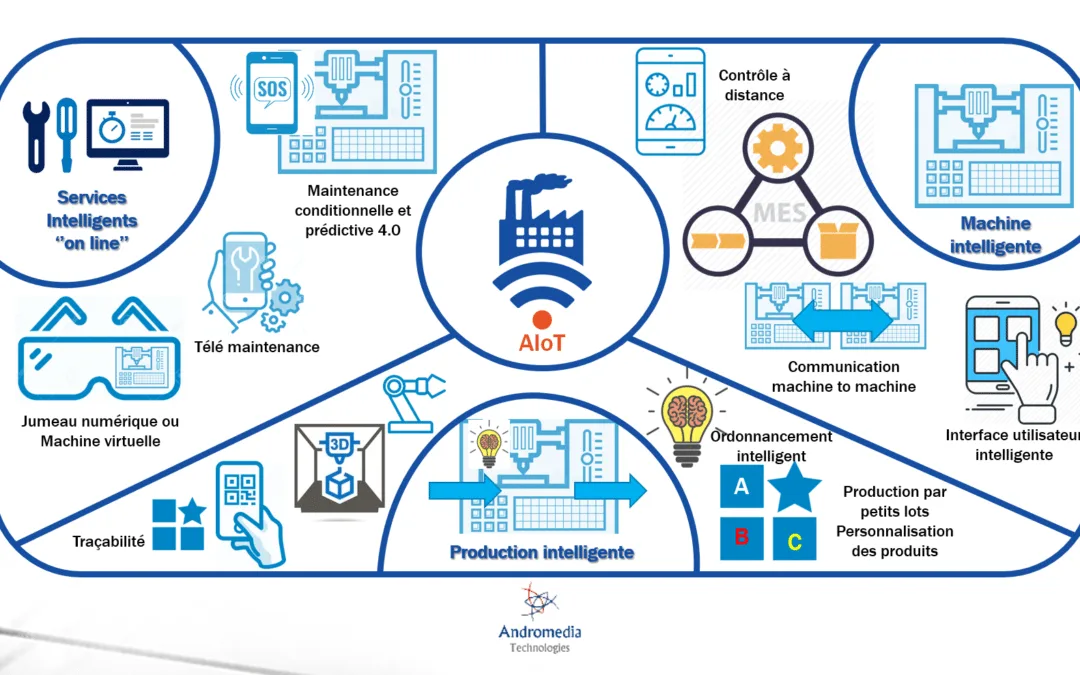
At the dawn of the digital revolution, the concept of smart factory emerges as the cornerstone of Industry 4.0. This radical transformation introduces the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced data analytics into manufacturing processes. In this context, Siemens stands out not only for its innovative approach but also for its concrete implementation, illustrating what it means to be at the forefront of this new industrial era.
Table des matières
ToggleArtificial Intelligence and Process Optimization
Siemens’ use of artificial intelligence in its factories reflects a significant upheaval in traditional production methods. For example, in its Amberg plant, Siemens has integrated a programmable logic controller that allows for real-time monitoring of machine performance. Through machine learning algorithms, the company analyzes the data generated to predict failures, thereby optimizing equipment availability. A recent study revealed that this method led to a 20% reduction in downtime, resulting in significant savings on operational costs.
Moreover, process improvement extends to the implementation of additive manufacturing, a technique that allows for the creation of custom and generally lighter parts, reducing material waste. According to a report from the Fraunhofer Institute, additive manufacturing could reduce production costs by 30% by 2025. By integrating such technologies, Siemens demonstrates how AI can transform the landscape of production, making factories not only more efficient but also more flexible.
Towards Horizontal Integration through IoT
The Internet of Things plays a central role in the digital transformation of manufacturing within Industry 4.0. Siemens leverages this technology to interconnect its machines and create an integrated network that optimizes production flows. Each machine potentially becomes a data point, providing valuable insights into performance and operational status. For instance, in 2023, Siemens launched a project in Nuremberg where each machine is equipped with IoT sensors that transmit real-time data on product quality, allowing for immediate correction of errors.
To reinforce this approach, Siemens has developed digital platforms capable of processing these data streams. Their predictive analytics tools allow for anticipating production rates and instantly adjusting processes to meet changing demand. According to data provided by Siemens, factories using this technology see a substantial improvement in their operational efficiency, with up to 15% growth in annual production. This shift towards horizontal integration demonstrates how an interconnected infrastructure enhances resilience and agility in businesses.
Strategies for Transitioning to Industry 4.0
The transition to Industry 4.0 is not without challenges, but Siemens offers a model to follow. For companies considering a shift to a smart factory, several strategies prove essential. First, a review of existing processes must be conducted to identify weaknesses and improvement opportunities. This initial assessment allows for the establishment of clear priorities for digital transformation.
Next, it is crucial to involve the entire staff in this transition. Continuous training programs and awareness workshops help prepare employees for new technologies and promote a culture of open innovation. At Siemens, internal skills development has led to a significant increase in productivity, as indicated by the results of a case study conducted in their factories.
Finally, the establishment of an agile system for continuous performance evaluation is essential. This allows for the adaptation of strategies as new technologies emerge and the market evolves. Siemens has also shown that an iterative approach to innovation, guided by measurable outcomes, can significantly reduce risk and maximize return on investment. In Uruguay, for example, the gradual scaling of certain data analytics tools resulted in a positive return on investment in less than two years.
By integrating these practical strategies, businesses can envision a successful transition to the era of the smart factory, while drawing inspiration from Siemens, which remains at the forefront of these revolutionary changes.
To deepen understanding of these dynamics, consult resources such as The Factory of the Future by Siemens and other studies on the evolution of Industry 4.0. Such exploration could provide even broader perspectives on the challenges and opportunities presented by this industrial revolution.
FAQ on Smart Manufacturing in the Era of Industry 4.0: Case Study on Siemens
What is the concept of smart manufacturing in Industry 4.0? Smart manufacturing is based on the integration of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence and IoT, enabling more efficient, flexible, and autonomous production.
How does Siemens position itself in Industry 4.0? Siemens stands out as a leader in Industry 4.0, offering innovative solutions to transform traditional factories into intelligent, connected production environments.
What are the main technologies used by Siemens? Key technologies include artificial intelligence, automation, advanced robotics, and data management systems, which enable continuous optimization of production processes.
What benefits does the adoption of Industry 4.0 bring to companies? The adoption of Industry 4.0 allows companies to improve productivity, reduce operating costs, gain agility, and offer customized products to their customers.
What challenges are associated with transitioning to a smart factory? Challenges include cybersecurity, the need to train staff in new technologies, and the seamless integration of existing systems with new digital solutions.
How does Siemens manage cybersecurity in its Industry 4.0 solutions? Siemens implements robust security protocols and regular updates to protect systems against cyber threats, ensuring data and operational security.
What concrete examples illustrate the impact of Industry 4.0 at Siemens? Projects such as the production of programmable logic control systems demonstrate how process optimization and automation can directly benefit the value chain.