When detection invades the industrial field, a new era is born, giving rise to Industry 4.0. This revolution radically transforms production processes through advances such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things, and automation. Merging the physical and digital worlds, this innovative industry redefines manufacturing methods by increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and improving process visibility. Despite its many advantages, the adoption of Industry 4.0 also poses challenges, particularly in terms of initial costs and the security of connected devices.
Industry 4.0 represents a significant advancement in the industrial sector by integrating intelligent digital technologies into production processes. This fourth industrial revolution is marked by interconnectivity, automation, and the use of technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IoT). Thanks to these innovations, factories become more connected, robotized, and intelligent, allowing for a noticeable improvement in production methods, productivity, and efficiency. Although the adoption of these technologies presents some challenges, including initial costs and security, it nevertheless transforms the industry towards a more sustainable and innovative future.
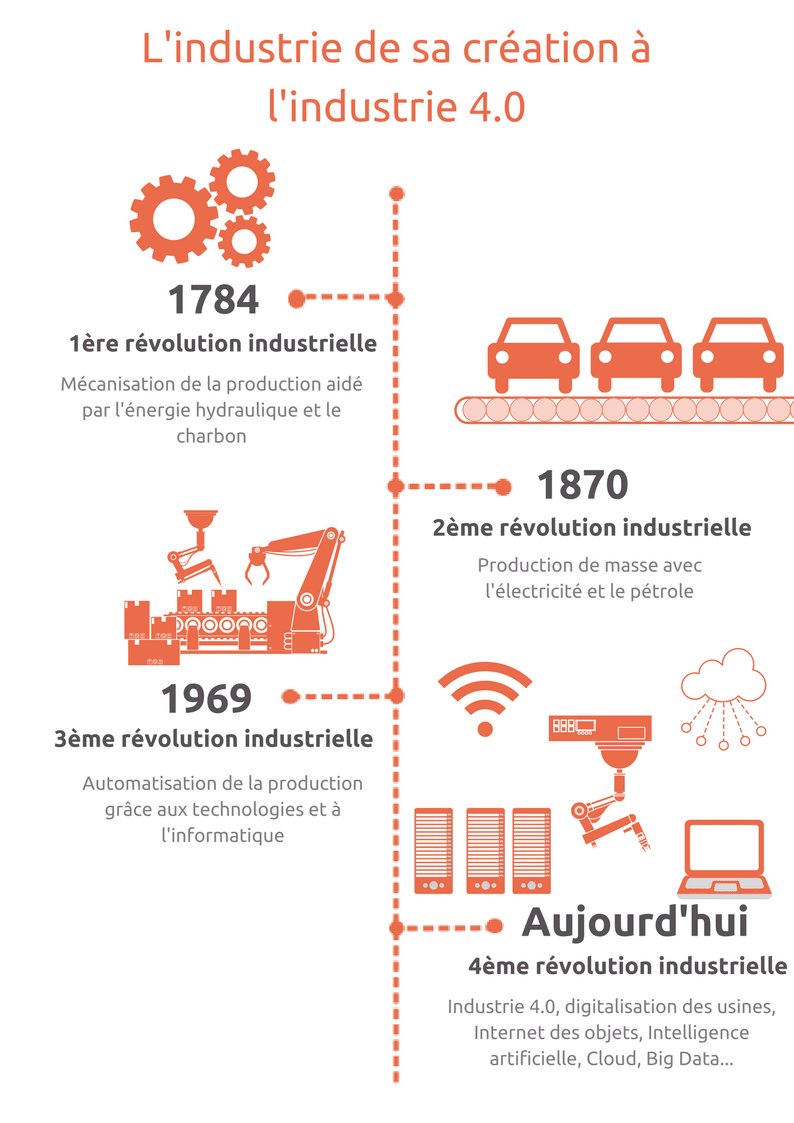
Table des matières
ToggleIndustry 4.0: a new industrial era
Industry 4.0 is essentially a fusion of the digital world with the physical world, thus transforming traditional production methods by integrating intelligent digital technologies. This new paradigm encompasses key concepts such as artificial intelligence, robotics, and automation, which together redefine how products are manufactured and distributed. This technological revolution enables unprecedented interconnection between machines, data, and systems, thus facilitating faster and more informed decision-making to avoid malfunctions and optimize production.
The technological components of Industry 4.0
In the era of Industry 4.0, technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and data analysis play a crucial role. Their applications are multiple: for instance, they monitor the health of machines, check product quality, and provide predictive maintenance to avoid costly interruptions. This technological transformation also relies on connected and automated production systems, often referred to as “cyber-physical,” creating an intelligent and agile production factory.
Challenges and prospects of Industry 4.0
The adoption of Industry 4.0 brings notable and considerable benefits, but it is not without challenges. Companies face high initial costs for implementing Industry 4.0 technologies, while issues of interoperability and the safety of connected devices remain common concerns. Despite these challenges, the future looks promising, with an expected reduction in costs and a gradual simplification of technology, making this digital revolution accessible to a broader range of companies. Experts anticipate significant growth in this sector, where the establishment of more agile and responsive production will become a major competitive advantage.




