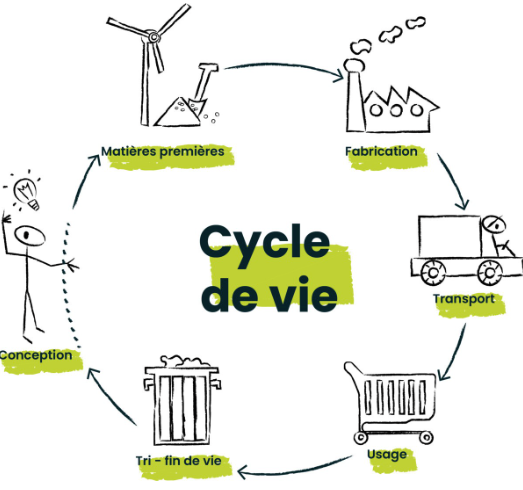
Make to Order, also known by its English terms Make To Order (MTO) or Build To Order (BTO), represents an innovative business model. This system is based on the principle of producing an item only when an order is placed, ensuring precise synchronization with the actual market demand. Far from traditional mass production methods, this approach limits inventories and reduces waste. It thus becomes a more eco-friendly manufacturing strategy tailored to the specific needs of consumers, allowing for increased customization and efficient resource use.
Make to Order, also known as Make To Order (MTO) or Build To Order (BTO) in English, is a revolutionary business model that transforms how products are manufactured in modern industry. Unlike traditional production methods, where massive stocks of products are created even before they are needed, make to order relies on the concept of producing only what is ordered. This means that the production of a product is triggered only after an order has been placed.
This model is closely related to the “Just-in-Time” (JIT) strategy, which relies on precise synchronization of production with actual market demand. By eliminating the need for excess inventories, make to order allows companies to reduce waste, improve operational efficiency, and minimize storage-related costs. This model is all the more relevant in the age of industrial automation and the sharing economy, where flexibility and adaptability are essential.
From an ecological standpoint, make to order is perceived as a sustainable strategy since it helps reduce resource waste, thereby limiting environmental impact. Producing only what the market needs helps avoid overproduction and unsold goods, which decreases the company’s carbon footprint. This approach fits into a sustainable logic that increasingly attracts industrial players concerned about their environmental impact.
Make to order often relies on the digital environment for its implementation. Technologies such as 3D printing, or additive manufacturing, play a crucial role by allowing the creation of physical objects from digital models. This process is distinguished by its ability to add layers of material to form a finished product, offering unprecedented flexibility compared to traditional production methods.
The concept of on-demand production is further reinforced by the integration of connected production systems and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), which enable smoother management and quick response to customer orders. Thanks to these technologies, companies can optimize their supply chain management, contributing to the overall improvement of modern industrial efficiency.
In addition to its economic and environmental advantages, make to order also encourages innovation. Companies are prompted to adopt new technologies, reorganize their production processes, and prepare for future trends, such as smart factories and smart contracts, to remain competitive. The link between innovation and on-demand production is therefore essential in the move towards Industry 4.0.
In summary, make to order is not just a production method; it is a true revolution in the modern manufacturing sector. By adopting this model, companies not only respond to market demand: they actively participate in building a more sustainable and efficient future while ensuring adaptability to the challenges of tomorrow.
Table des matières
ToggleFrequently Asked Questions: Make to Order
Q: What is make to order?
A: Make to order, also known by its English names Make To Order (MTO) or Build To Order (BTO), is a business model where a product is manufactured only when it has been ordered by the customer.
Q: Why is make to order considered eco-friendly?
A: This approach limits the production of products in excessive quantities, which reduces waste and optimizes resource use.
Q: How does make to order work?
A: It works by creating a physical object from a digital model, often by adding layers of material, when actual market demand requires it.
Q: What are the economic advantages of this model?
A: Make to order aligns production with the real needs of customers, thus reducing costs associated with storing surpluses or unused products.
Q: What technologies facilitate make to order?
A: The integration of the Industrial Internet of Things, the use of advanced digital systems, and additive manufacturing tools are essential for efficiently responding to on-demand orders.