The era of smart factories is a true revolution that challenges the standards of Industry 4.0. Digital transformation, making production processes more connected and optimized, brings remarkable flexibility to businesses. However, this rapid advancement does not come without its challenges. The obstacles to overcome are numerous and varied, ranging from technical issues to personnel training concerns. As technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things contribute to this new era, industries face problems such as cybersecurity, system interoperability, and a lack of qualified human resources.
The implementation of these innovative solutions is anything but simple. Many sectors, such as automotive and aerospace, are trying to juggle these challenges while seeking to leverage the advantages offered by Industry 4.0. Analyzing these obstacles is essential to understanding how companies can not only adapt to this revolution but also benefit from it to ensure their competitiveness and sustainability in the global market.

The evolution towards Industry 4.0 has revolutionized the global industrial landscape, highlighting the concept of the smart factory. This transformation relies on the integration of advanced technologies, such as Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time data analytics. However, despite the undeniable advantages it presents, the widespread adoption of smart factories faces several significant obstacles that are crucial to analyze. This article explores the main challenges and offers recommendations for ensuring a successful transition to Industry 4.0.
Table des matières
ToggleThe Stakes of Industry 4.0: Towards a Technological Revolution
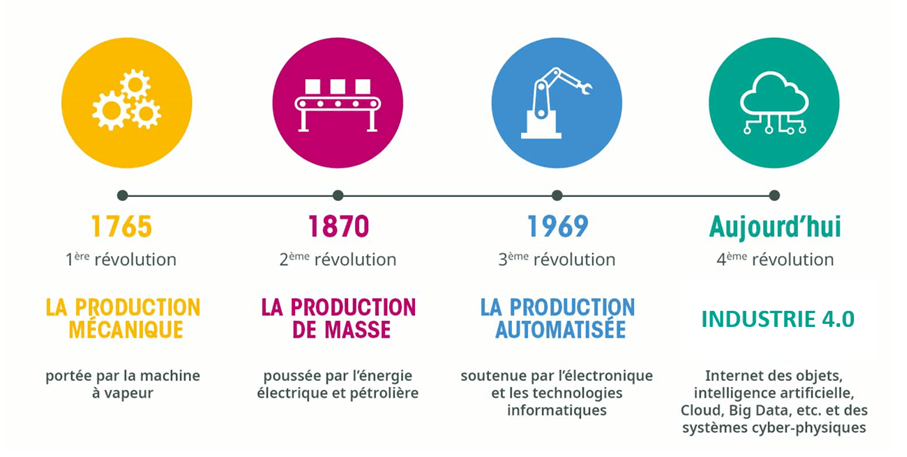
The term Industry 4.0 refers to the fourth industrial revolution, characterized by the automation and digitization of production processes. According to a recent study by the Institute for Research in Industries, the global market for technologies related to Industry 4.0 could reach USD 1,203.38 billion by 2033, reflecting the growing importance of this innovation.
The advantages of smart factories are numerous, including process optimization, reduced production costs, and improved product quality. By integrating interoperable systems, companies can respond more quickly to market changes, thereby strengthening their competitiveness. However, these gains do not come without challenges.
Among the main difficulties are the lack of knowledge and technical skills within the workforce. According to a report by Oracle, 54% of executives claim that the lack of trained staff to manage this transition poses a significant barrier. Additionally, companies must invest heavily in upgrading their existing systems, which requires substantial financial and human resources.
Technical Obstacles and Adaptation Strategies
One of the main technical obstacles encountered by companies during the adoption of smart factories is the issue of cybersecurity. With the increased interconnection between machines and systems across the web, factories become vulnerable to cyberattacks. A study conducted by McKinsey revealed that nearly 80% of companies in the manufacturing sector have suffered a cybersecurity attack in the past two years.
To address this vulnerability, it is crucial to incorporate robust security protocols from the design stage of the systems. Companies must invest in advanced cybersecurity solutions such as predictive analytics and intrusion detection systems. Furthermore, training staff on cybersecurity is an essential step. Indeed, awareness and continuous training represent one of the best defenses against cyber threats.
Another obstacle is the scarcity of relevant data needed to feed the necessary analyses. To overcome this difficulty, a cloud computing-based approach can be beneficial. Solutions like the collaborative platform described in the analysis of inoindustry allow diverse actors to unite their forces to access more comprehensive and higher-quality data sets.
Future Prospects and Key Innovations
The future of smart factories relies on continuous innovation. By leveraging data collected via embedded sensors, artificial intelligence can enhance decision-making at various levels, from quality control to logistics. For instance, companies like BMW and Intel are collaborating to implement AI in their processes, allowing for the exploration of new ways to improve productivity while reducing waste.
Promoting an ecosystem of open innovation is also essential. By bringing together universities, research centers, and companies through co-creation initiatives, it becomes possible to develop solutions tailored to the unique challenges of each sector. This not only allows for sharing the costs of research and development but also accelerates the innovation process.
Finally, adopting a learning-oriented culture is fundamental as well. Implementing continuous training and promoting e-learning can prepare the workforce for future challenges. In France, several initiatives, such as those discussed in the article by Scancap, illustrate how companies can benefit from ongoing education in digital technologies.
Testimonies from leaders who have already embraced Industry 4.0 highlight the importance of a strategic approach. A striking example is Cargill, a company that has received the Smart Factory Award for its commitment to digital transformation.
In conclusion, the advancement of smart factories within Industry 4.0 represents both a challenge and an opportunity. Although the obstacles are real, solutions exist, and companies can capitalize on this new revolution provided they adopt appropriate and innovative strategies.

La sécurité des usines intelligentes : comprendre comment éviter les attaques basées sur l'identité https://t.co/V7d1rnXnLe
— Virginie Mollet (@VirginieMollet) July 4, 2023
FAQ on the Advancement of Smart Factories in Industry 4.0
What is a smart factory? A smart factory is a production environment that integrates digital technologies and interconnected systems to optimize manufacturing processes and improve operational efficiency.
What are the main obstacles to the adoption of smart factories? The main obstacles include cybersecurity, the high cost of technologies, staff training, and the integration of existing systems.
How can the challenges of cybersecurity in Industry 4.0 be overcome? To overcome these challenges, it is essential to deploy interoperable systems and establish robust security protocols to protect sensitive data.
What role does artificial intelligence play in smart factories? Artificial intelligence enables real-time data analysis, process optimization, and informed decision-making to enhance productivity.
Why is it important to train staff for Industry 4.0? Continuous training is crucial as it allows staff to adapt to new technologies and maximize the potential of the digital tools deployed in the factory.
What are the benefits of transitioning to Industry 4.0? Benefits include improved efficiency, cost reduction, better operational flexibility, and an increased ability to respond to market demands.
How can e-learning assist in this transition? E-learning allows employees to access up-to-date training resources and learn at their own pace, thus facilitating adaptation to changes.