Table des matières
ToggleApplications of Industry 4.0 in the Electronics Field
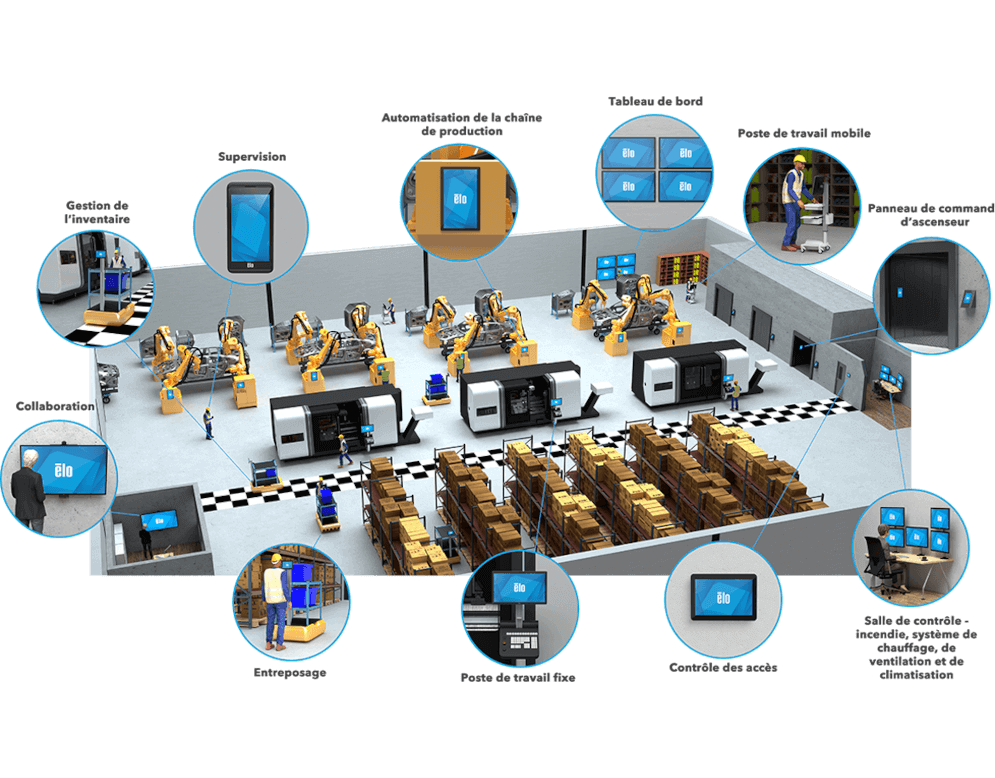
The Industry 4.0 revolution has led to significant transformations in the field of electronics. By integrating technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and advanced automation, the electronics industry is now experiencing a significant increase in productivity and efficiency.
Applications of Industry 4.0 in the Electronics Field:
Smart factories use connected sensors to collect and analyze data in real-time. This provides an overview of ongoing operations and enables informed decision-making to optimize production processes.
Predictive maintenance is another key application. By analyzing data collected from sensors, predictive systems can identify potential failures before they occur, thereby reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
With the integration of AI, production processes can be automated and continuously improved. Machine learning algorithms allow machines to self-adjust to maximize efficiency and product quality.
Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies also offer benefits for training and design. Technicians and engineers can use AR and VR to visualize and interact with 3D models, thereby facilitating prototype development and training on complex equipment.
- Automation of production lines: improving speed and accuracy.
- Real-time monitoring: rapid detection of anomalies and inefficiencies.
- Optimized resource management: reducing waste and energy costs.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 brings innovative solutions that transform all aspects of the electronics sector, from design to production through maintenance.
Automation of Manufacturing Processes
The Industry 4.0 represents a major transformation in the field of electronics. It integrates advanced technologies to improve the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing processes. Companies are adopting these innovations to remain competitive in the market.
Among the key innovations are the Internet of Things (IoT), digital twins, and artificial intelligence (AI). These technologies enable real-time monitoring, better resource management, and more informed decision-making.
The management of the supply chain is also revolutionized by Industry 4.0. Through connected systems, companies can track materials and products from production to delivery, thereby reducing lead times and errors.
- Improvement of process accuracy.
- Reduction of downtime through predictive maintenance.
- Optimization of resource usage.
The automation of manufacturing processes is a central pillar of Industry 4.0 in electronics. Robots and automated systems replace many manual tasks, thereby increasing accuracy and speed of production.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside humans to perform complex tasks. They are programmable and easily reconfigurable, making them ideal for flexible production processes.
Additionally, computer vision systems are widely used to inspect electronic components with high precision. These systems detect and correct defects in real-time, ensuring a high level of quality.
Interconnectivity of Equipment
Industry 4.0 is radically transforming the electronics sector through the integration of advanced technologies. Numerous applications are emerging, increasing efficiency and productivity.
Applications of Industry 4.0 in the Electronics Field
The applications of Industry 4.0 are varied and offer distinct advantages. Among the most notable:
- Automation and robotics: improving manufacturing processes.
- Predictive maintenance: reducing downtime through real-time data analysis.
- Flexible production lines: rapid adaptation to market changes.
- Quality and traceability: precise tracking of components and finished products.
Interconnectivity of Equipment
Industry 4.0 relies on the interconnectivity between machines and systems. Communication between equipment is facilitated by the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing for real-time data collection and optimization of operations.
This interconnectivity allows for precise data on machine performance, identifying defects, and scheduling maintenance interventions without disrupting production lines.
Furthermore, sensors and smart devices play a crucial role in integrating analytics and automated decision-making, thereby enhancing the responsiveness and reliability of production systems.
“`