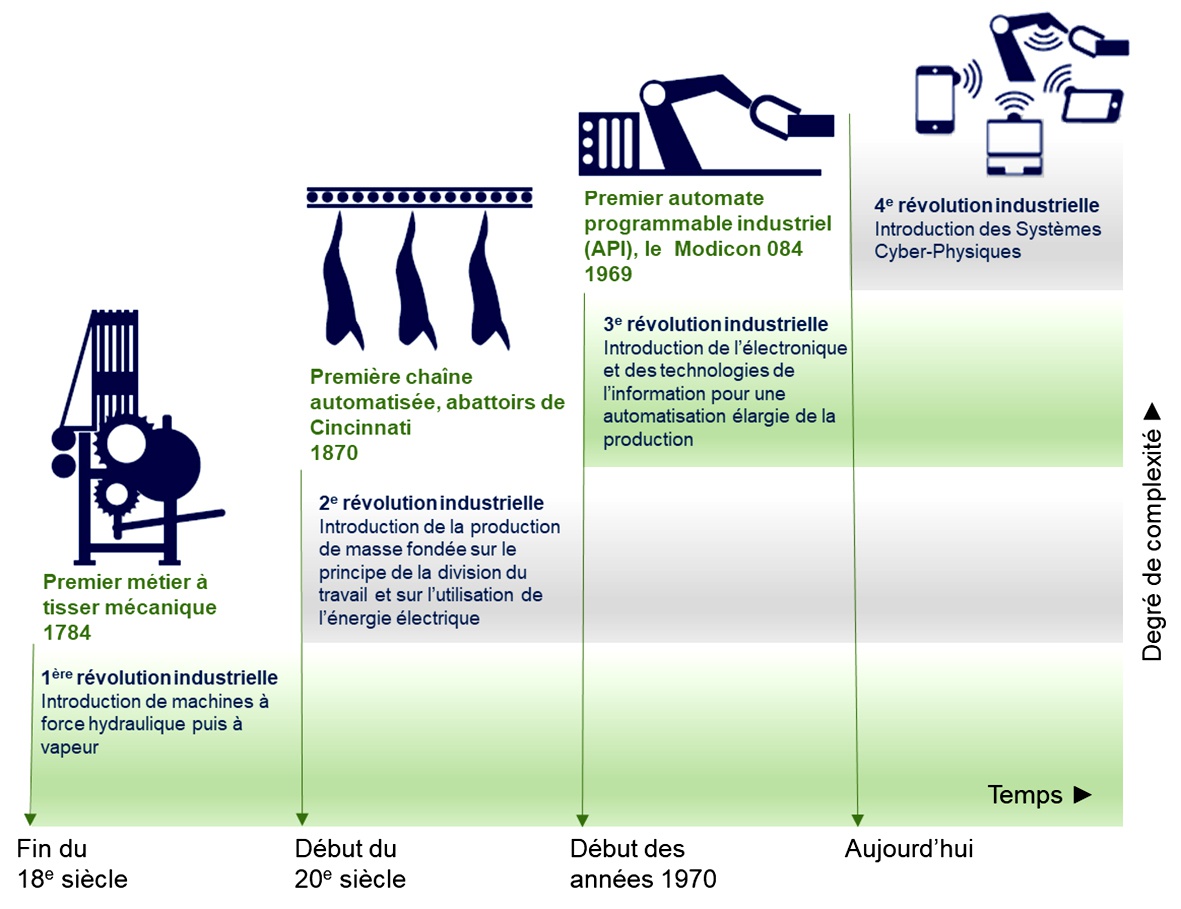
Industry 4.0, characterized by advanced automation, IoT, and artificial intelligence, is profoundly transforming the world of work. Its goal is to rapidly respond to customer needs while respecting the environment and keeping humans at the center of processes. This technological evolution is revolutionizing manufacturing, distribution, and storage, while redefining the skills required in areas such as maintenance, computing, and data science. Frontline workers are seeing their jobs evolve towards more technical and interconnected roles, requiring continuous training and rapid adaptation to new technologies.

Revolutionizing the industrial sector, Industry 4.0 integrates cutting-edge technologies such as automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence. This article explores the main challenges of this technological evolution, as well as its major impacts on frontline workers, particularly in terms of required skills and training.
Table des matières
ToggleThe Challenges of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, also known as the fourth industrial revolution, is based on the integration of advanced technologies into production processes. It aims to improve efficiency, flexibility, and responsiveness to customer needs while respecting the environment and placing humans at the center of concerns. Among the major challenges are the standardization of processes, data security, environmental sustainability, and preserving the role of humans in industry.
Impacts on Jobs
The digitization and increasing automation of industry are transforming jobs. Smart machines and collaborative robots, also known as cobots, work alongside human operators, creating a new configuration of workstations. Communication between humans and smart machines becomes essential to ensure smooth and efficient production.
The Jobs and Skills of Tomorrow
This radical transformation generates an increased need for specialized skills. Frontline jobs, such as maintenance, computing, data science, quality control, and human resources, must adapt to Industry 4.0 technologies. Workers must master new technologies and be trained in the latest advancements to remain competitive in the job market.
Optimization of Operations
Industry 4.0 technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), enable the connection of production devices for real-time monitoring. This interconnectivity optimizes operations, reduces downtime, and improves product quality. However, it also requires skills in data analysis and connected systems management.
Training and Skills Development
In response to this technological shift, ongoing training of employees becomes imperative. Companies must invest in training their workers to prepare them for the challenges of Industry 4.0. This includes technical training programs, as well as initiatives aimed at developing cross-functional skills such as complex problem solving and collaboration.
Environmental and Societal Challenges
By integrating cleaner and more efficient technologies, Industry 4.0 contributes to environmental sustainability. However, it also raises societal questions, particularly regarding the ethics of data usage and the impact on employment. Ensuring a just transition, where the benefits are equitably shared, remains a major challenge.
Industry 4.0 is a tremendous opportunity to revolutionize the industrial sector, but it also poses significant challenges. Frontline workers must adapt to a rapidly evolving technological environment, acquire new skills, and benefit from ongoing training to remain relevant and effective in their roles. Companies, for their part, must navigate this transformation carefully, considering the economic, environmental, and human implications.
- Environmental challenges: Reduce ecological footprint and promote sustainable development.
- Increased automation: Introduction of robotics and smart machines to optimize operations.
- Human-machine communication: Create a smooth interface between employees and advanced technologies.
- Specialized skills: Emphasizing maintenance, computing, data science, and control.
- Ongoing training: Adapting the workforce to the latest technological advancements.
- Predictive maintenance: Anticipating repair needs through real-time data.
- Production optimization: Integration of new processes to improve efficiency.
- Data security: Ensuring protection of information in a connected environment.
- Standardization of processes: Uniforming methods to facilitate interoperability.
- Impact on employment: Transformation of traditional jobs and emergence of new roles.
Vers une industrie 4.0 : synergies entre informatique durcie, automation et communication https://t.co/Xez3lArHxv
— Futura (@futurasciences) July 15, 2024
“`