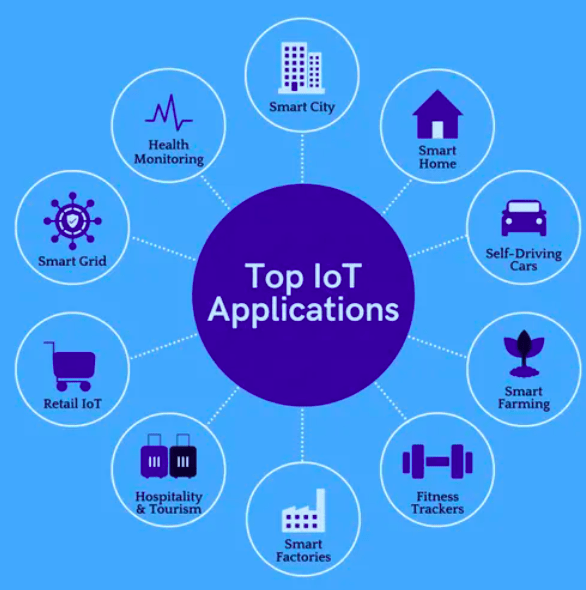
The Internet of Things (IoT) stands out for its ability to connect physical objects through the web, ranging from sensors to complex devices. This network creates a constant flow of data allowing for smooth communication between devices. Embedded sensors and data analytics platforms form the backbone of this technology, transforming the way real-world information is captured and used. By integrating sensors and actuators, IoT offers a revolutionary interconnection between objects, places, and environments, driving a new era of innovation and efficiency.
Table des matières
ToggleUnderstanding the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a concept that has transformed our way of understanding and interacting with the technological world. IoT refers to the interconnection of physical objects via the Internet, allowing these objects to exchange data without human intervention. Through the integration of sensors, software, and other technologies, IoT creates a network of smart objects capable of collecting and analyzing data in real-time.
The three fundamental elements of IoT include sensors, communication networks, and data analytics platforms. Sensors embedded in objects capture information about the physical environment, while communication networks enable the transfer of this data to servers or cloud platforms. Finally, analytics platforms process the data to provide valuable insights to users.
With the advent of IoT, the industry has seen a massive transformation with entire sectors adopting this technology to optimize their operations. For example, in the manufacturing sector, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) plays a crucial role by enabling predictive maintenance, improving operational efficiency, and implementing the principles of Industry 4.0.
The impact of IoT on Industry 4.0 is significant. Advanced digital technologies transform manufacturing methods by making processes smarter and more efficient. As indicated in this article market revolution of Industry 4.0, the integration of IoT into production lines not only reduces costs but also improves product quality and reliability.
Another valuable application of IoT lies in the utility and infrastructure sectors, where this technology enables the development of smart cities. By utilizing IoT for energy management, environmental monitoring, and waste management, cities can become more sustainable and offer a better quality of life to their citizens.
The challenges related to the adoption of IoT include data security, system interoperability, and the complexity of technological integration. However, with initiatives led by companies like Cisco partnering with governments to promote IoT, as illustrated in this initiative, the barriers are beginning to fade.
In conclusion, the potential of the Internet of Things is immense. Companies that understand and adopt this technology can benefit from the opportunities offered by IoT, whether in lean production, optimizing supply chains with smart contracts, or creating innovations in various sectors. To learn more about the impacts of IoT in the context of the current industry, check out this in-depth analysis.
Understanding the Internet of Things (IoT)
Q: What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
A: The Internet of Things, or IoT, refers to the network of physical objects connected to the Internet equipped with sensors. This allows them to collect and exchange data.
Q: How does the Internet of Things work?
A: IoT works through the integration of sensors and software into physical objects. These components facilitate communication and data transfer between devices via the Internet.
Q: What are the key elements of IoT?
A: IoT mainly consists of three key elements: sensors or connected devices, communication networks, and data analytics platforms.
Q: What types of technologies are used in IoT?
A: Technologies used in IoT include sensors for capturing data from the real environment and actuators that execute actions based on the collected data.
Q: What is the main goal of IoT?
A: The main goal of IoT is to improve operational efficiency, resource management, and production based on data collected and analyzed in real time.