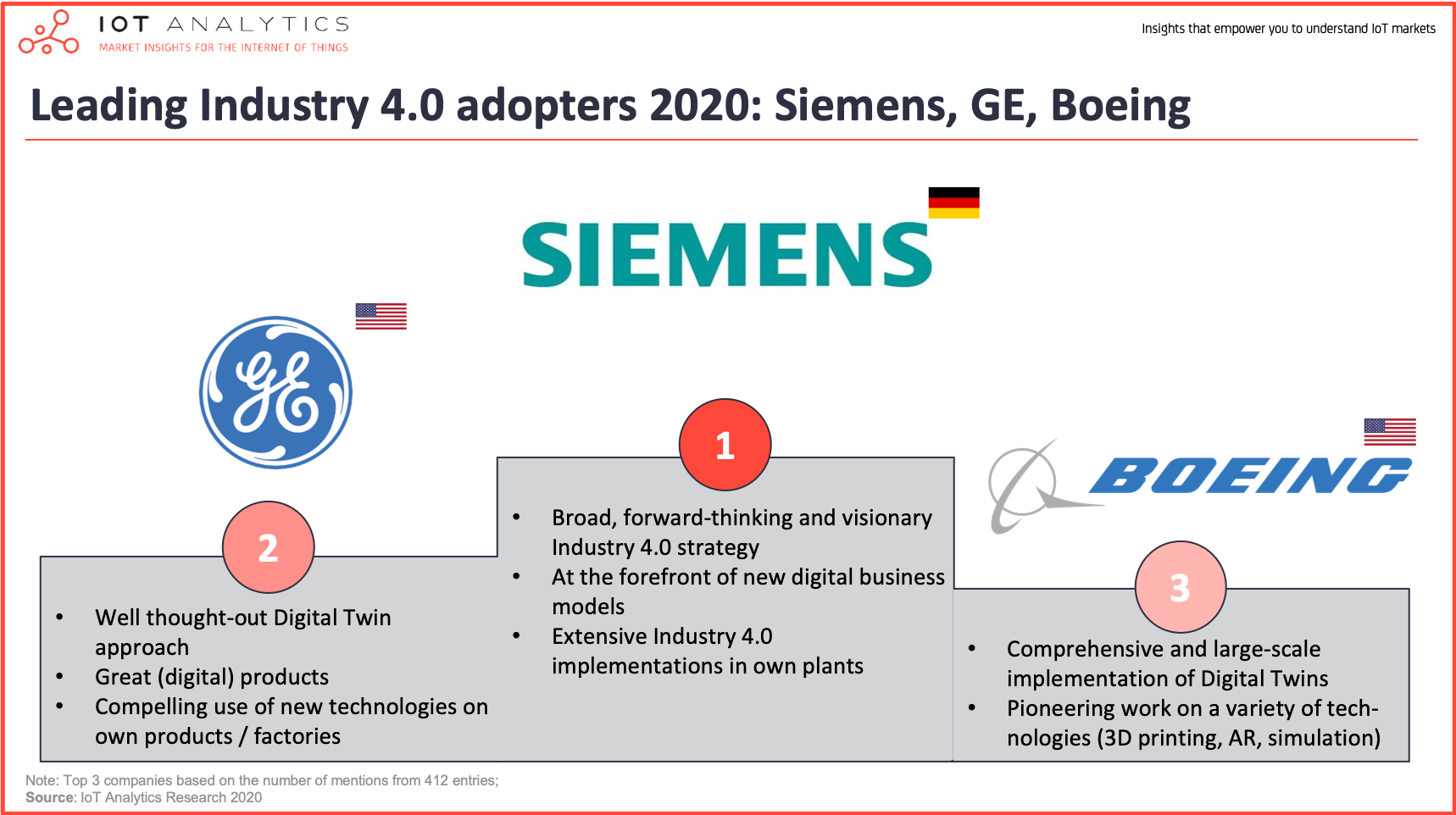
The adoption of Industry 4.0 marks a crucial step for any manufacturing company looking to remain competitive and innovative. Initially introduced in Germany in 2011, this industrial revolution is based on the digiţalization of production processes. By integrating advanced technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things (IIoT), Industry 4.0 promises to significantly improve productivity, efficiency, and the quality of manufactured products. Considering the adoption of these technologies should occur when a company assesses its needs for automation and optimization, as well as its ability to transform its existing infrastructure.
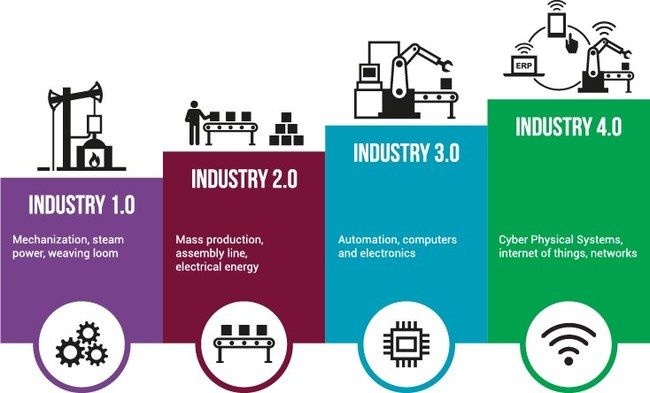
Industry 4.0, or the fourth industrial revolution, marks a major technological transformation in the manufacturing sector. This revolution is characterized by the integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and integrated computing systems. So, when exactly should a company consider adopting these new technologies? This article explores the clues and key moments that indicate it is time to transition to Industry 4.0.
Table des matières
ToggleRecognizing signs of stagnation
When productivity and efficiency of processes begin to stagnate or decline, it may be a sign that it is time to adopt Industry 4.0 solutions. Smart and collaborative tools enhance performance and help overcome these challenges. Advanced technologies also provide methods to improve manufacturing quality.
The growing complexity of customer demands
Today’s customers seek increasingly customized and high-quality products, delivered in ever-shorter timeframes. When the demand for such products grows and your current production reaches its limits, adopting Industry of the Future technologies can give you the agility necessary to meet these expectations. Integrating digital systems allows better management of customized orders and improves the flexibility of production lines.
Increasing competition
In a competitive market, failing to adopt the innovations of Industry 4.0 can put you at a disadvantage against competitors. If your partners and rivals are integrating connected solutions to improve their productivity while reducing costs, it becomes crucial to keep pace to stay competitive.
The availability of resources and skills
Another key factor is the availability of financial and human resources. The adoption of advanced technologies requires substantial investments and a skilled workforce for their implementation and management. When your company has these resources, it might be the right time to start the transition to a connected factory.
Government grants and incentives
Some governments offer grants and tax incentives to help businesses integrate 4.0 technologies. Taking advantage of these opportunities can significantly reduce initial costs and accelerate the return on investment. Keep an eye on the support programs available in your region to determine the right moment.
Avoiding skilled labor shortages
Adopting Industry 4.0 can also be a response to the shortage of skilled labor. With advanced automation and intelligent systems, you can maintain a high level of production even when human skills become scarce. These technologies also enable the training of a new workforce by enhancing the skills of current employees.
Preparing for unforeseen events
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of resilience in production chains. Adopting digital technologies allows for real-time monitoring, remote management, and increased responsiveness to disruptions. If your company seeks to strengthen its resilience against unforeseen events, Industry 4.0 offers suitable solutions.
Ecology and sustainability
Environmental concerns are driving more companies to rethink their manufacturing processes. Industry 4.0 technologies can improve energy efficiency and reduce waste, contributing to more sustainable practices. If sustainability is a priority for your company, adopting these technologies can help you achieve your ecological goals.
- Ongoing digital transformation: When your company is already engaged in a digitalization of its processes.
- Improvement needs: If you are looking to enhance productivity, efficiency, and quality of your manufacturing operations.
- Competitiveness: To remain competitive in a market where industry giants are adopting these new technologies.
- Training the workforce: When it becomes necessary to train your staff to be more skilled and adaptive to new technologies.
- System integration: If the integration of computing and collaborative systems becomes a pressing need.
- Automation: When you consider automating not just production but also the automation processes themselves.
[#Industrie 4.0] : 🔋 Les entreprises adoptent des systèmes de gestion énergétique basés sur l'IA pour réduire les gaspillages, optimiser les processus et baisser les coûts. Un pari sur l'avenir ! Une analyse d'@a_voygillis @IAEPoitiers > https://t.co/OkJaQuicSD#industrie pic.twitter.com/Q3TTk3puRj
— Xerfi Canal (@XerfiCanal) March 15, 2024
“`